Mouth Cancer
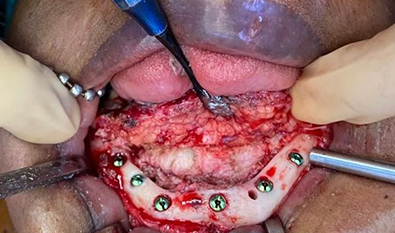
Mouth Cancer
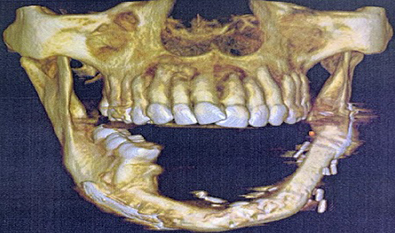
Mouth Cancer
As a society, RGCIRC is looking forward to get support from generous people
Read MoreIt is a fact that there are absolutely no substitutes to replace human bloo...
Read MoreVolunteers play an important role in today’s hospitals. They help the hos...
Read MoreRajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute & Research Centre is today counted amongst Asia’s premier exclusive cancer centres that offer unique advantage of cutting edge technology, put to use by renowned super specialists. This potent combination of man and machine ensures world-class cancer care to not only patients from India, but also from the neighboring SAARC countries and others.
D - 18, Sector - 5, Rohini, Delhi - 110085 | +91-11-47022222 OPD Timings: 09:00 am to 05:00 pm (All weekdays except Sunday and Holiday) Emergency Services: 24x7 All weekdays
Mahendra Kumar Jain Marg, Niti Bagh, New Delhi - 110049 | Tel: +91-11-45822222 / 2200 OPD Timings: 09:00 am to 05:00 pm (All Weekdays except Sunday and Holiday) Emergency Services: 24x7 All Weekdays